Overview of Blockchain
In the digital age, blockchain has emerged as one of the most revolutionary and promising technologies. But what exactly is blockchain, and how does it work? In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of this innovation,providing an overview for beginners.
Definition of Blockchain: A Decentralized Ledger
Blockchain is a type of digital ledger that records transactions securely, transparently, and in a decentralized manner. Unlike traditional centralized databases, blockchain operates on a network of computers (nodes) distributed across the world. Each node holds a copy of the entire ledger, making the system resistant to manipulation and corruption.
How Does Blockchain Work?
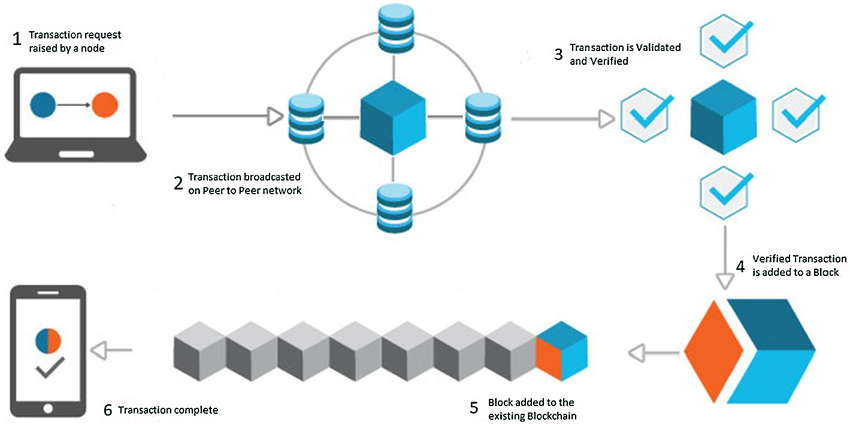
Imagine a public and shared ledger, divided into blocks of information. Each block contains a set of recent transactions and a cryptographic reference to the previous block. The connection between blocks through cryptography creates a chain, hence the term blockchain.
Decentralization and Security
Data is distributed among all nodes in the network instead of being stored centrally. This eliminates the risk of a single point of failure and makes data manipulation extremely difficult.
Network Consensus
To add a new block to the chain, the majority of nodes must agree on the validity of new transactions. This process, known as network consensus, ensures that the information is accurate and accepted by all participants.
Cryptocurrency and Mining
Some blockchains, like Bitcoin, use a reward system called "mining" to validate and add new blocks. Miners solve complex cryptographic problems, earning new digital tokens as a reward for their work.
Data Immutability
Once a block is added to the chain, modifying it is extremely difficult. Every subsequent block depends on its integrity, creating an immutable structure.
Blockchain Use Cases: Beyond Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain has evolved beyond its original role as cryptocurrency infrastructure, expanding into various industries. Here are some examples:
Smart Contracts
Self-executing programs that automatically fulfill contract conditions when predefined criteria are met.
Supply Chain and Traceability
Securely recording every step in a product’s supply chain to ensure quality and origin.
Identity Management
Creating secure systems for managing digital identities.
Healthcare
Enabling secure sharing of medical data among different healthcare providers.